美援臺灣建設規劃地圖與經費分配表
US aid to Taiwan: maps for the planned constructions and industrial development, with budgeting instructions
1953 ✦ ──── 民國 42 年 the 42th year of Republic of China era
1945年第二次世界大戰之後,日本戰敗,臺灣光復,由當時的國民政府治理臺灣。因為二次世界大戰期間的空襲轟炸,臺灣處處受創,因此,光復初期,政府重建與發展臺灣社會的所需經費龐大。幸而自1950年起有來自美國政府的美援挹注,使臺灣的多種建設,得以在「中美合作」之下,逐步順利推進。
所謂「美援」,其對臺灣的幫助是有規劃的:由美國的「經濟合作總署中國分署」(Economic Cooperation Administration, Mission to China,簡稱ECA)與「行政院美援運作委員會」(簡稱美援會)共同運作,進行各種建設工作。「經濟合作總署中國分署」後來於1951年改稱為「美國共同安全總署中國分署」(Mutual Security Mission to China,簡稱MSA),於1953年又改稱為「國外業務總署」(Foreign Operations Administration, 簡稱FOA)。因此,有甚多美援相關的規畫文件,分別出現ECA、MSA、FOA 等不同的名稱。
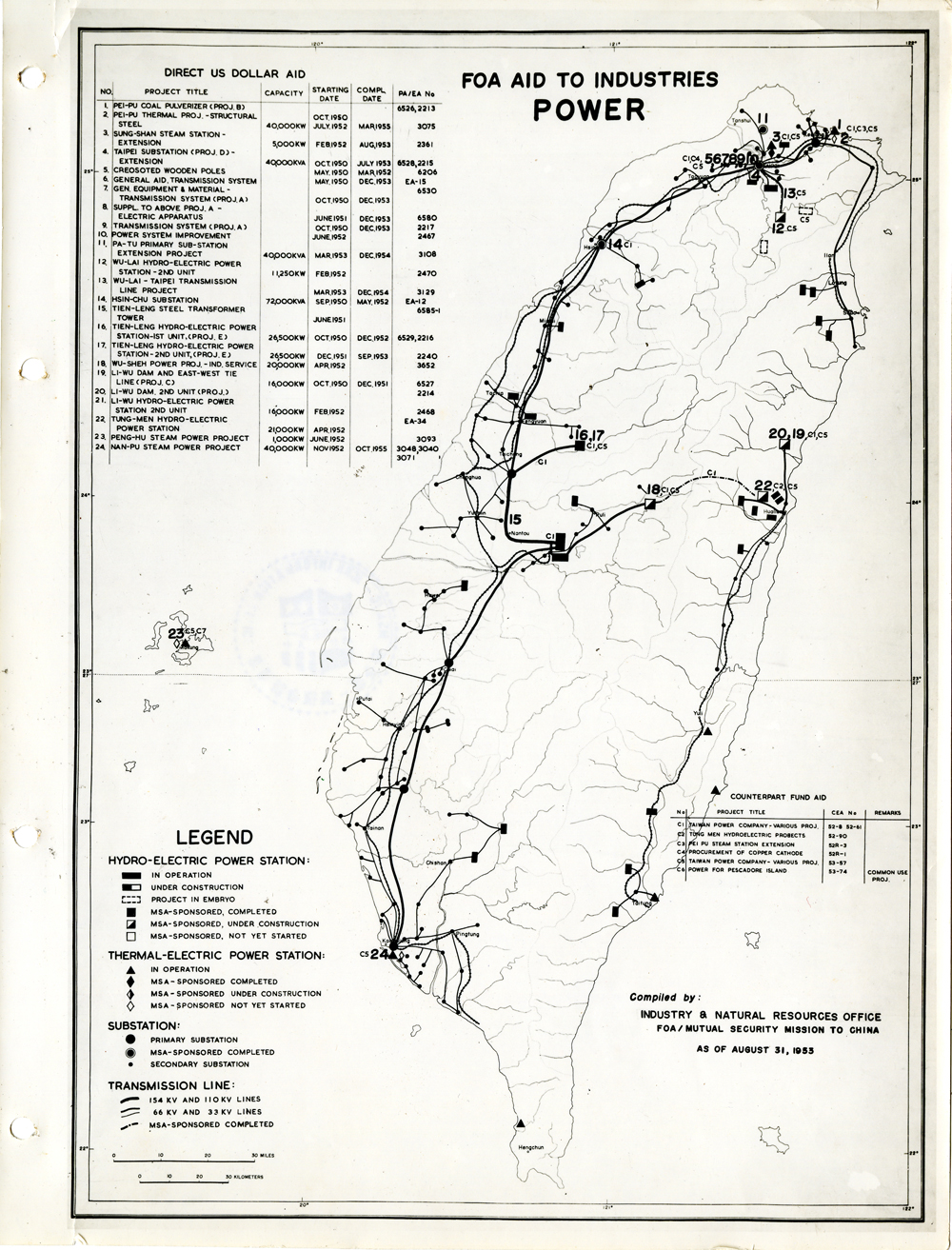
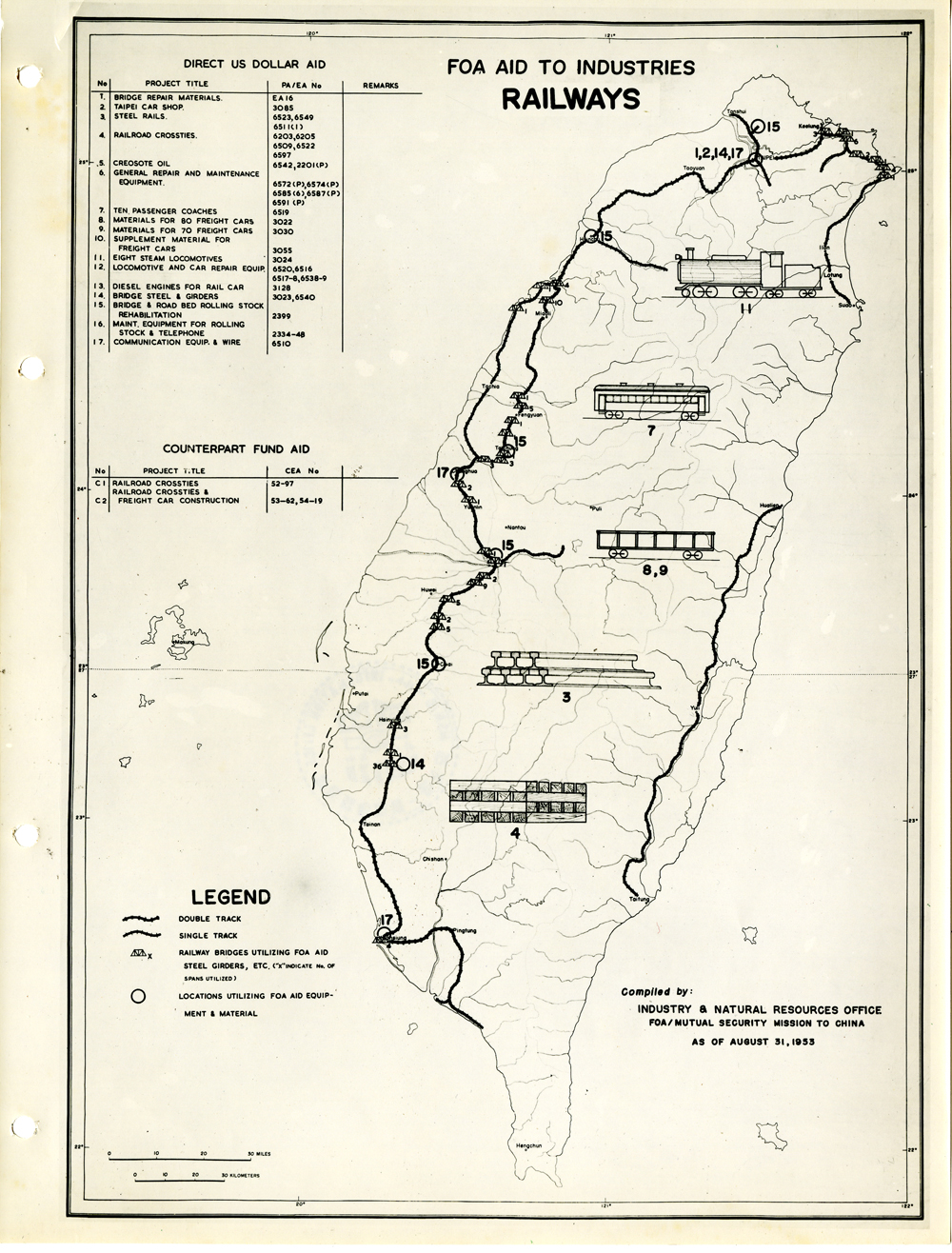
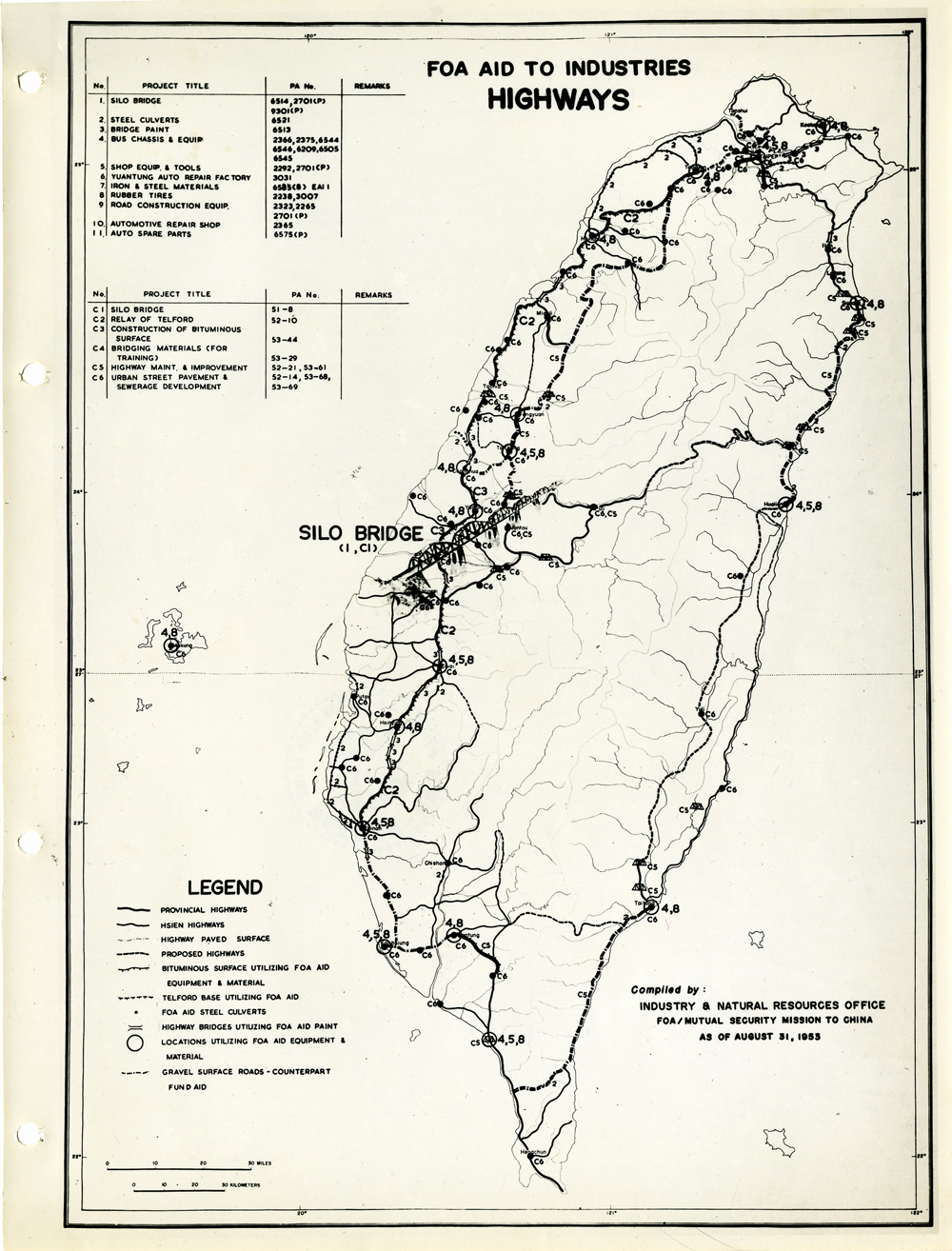
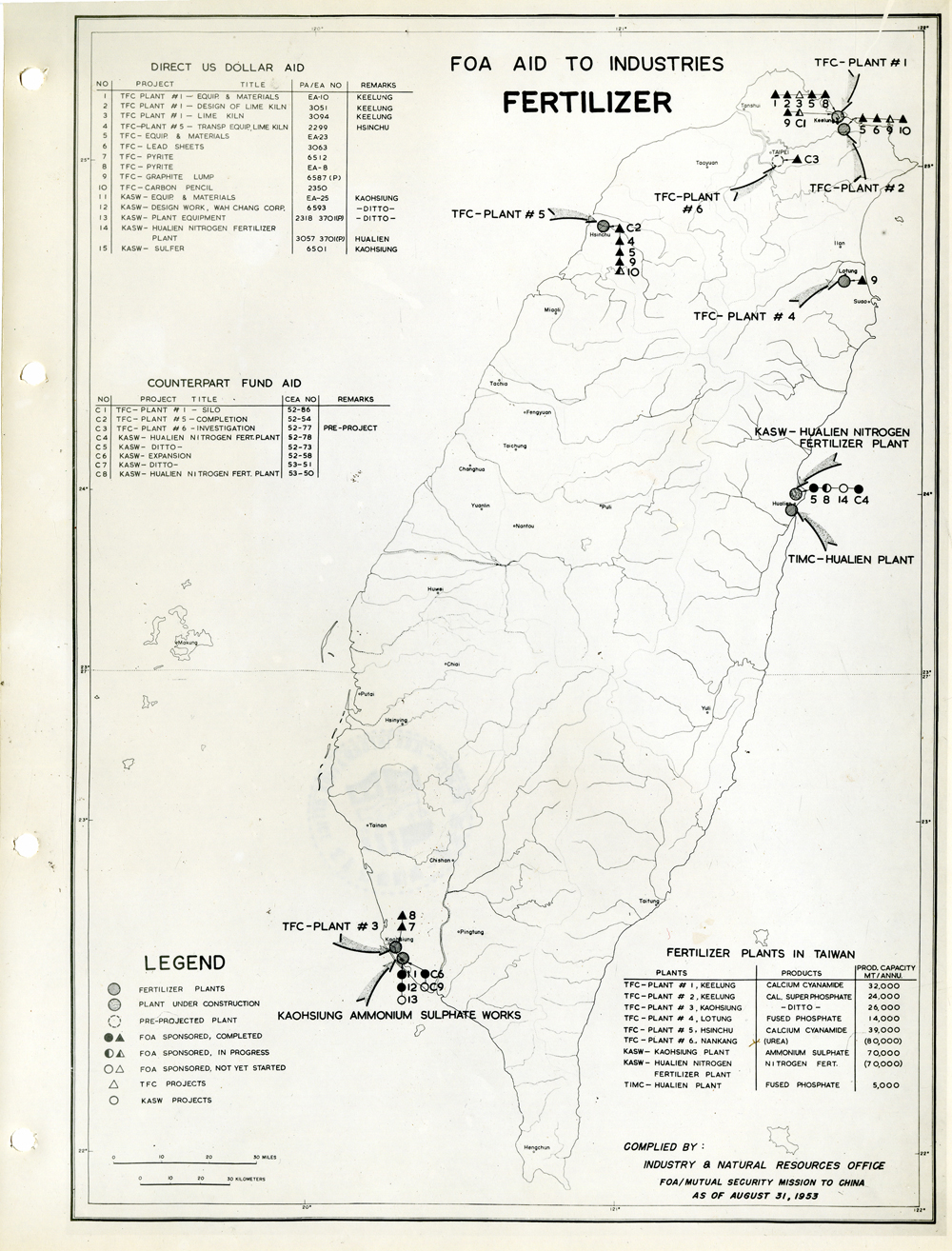
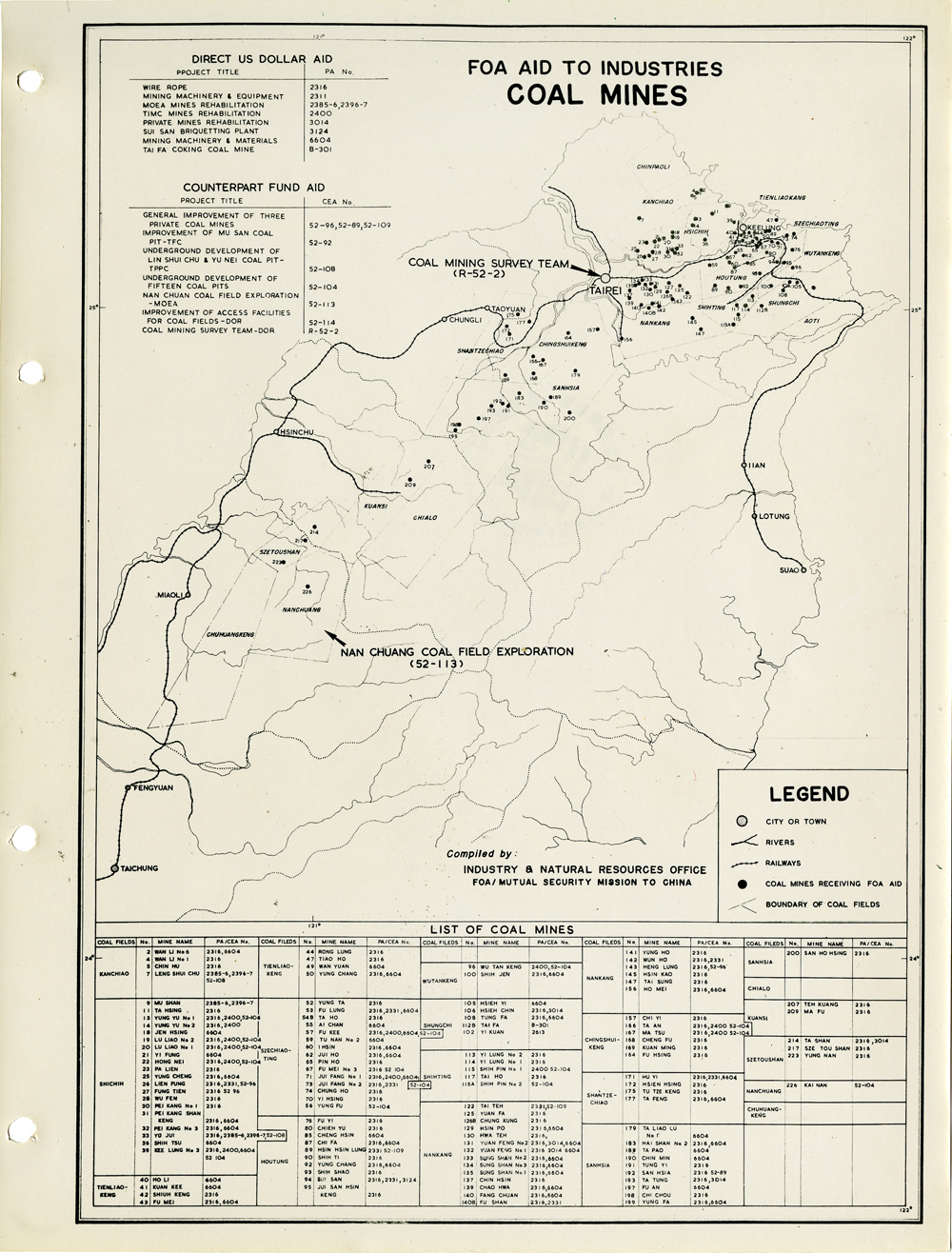
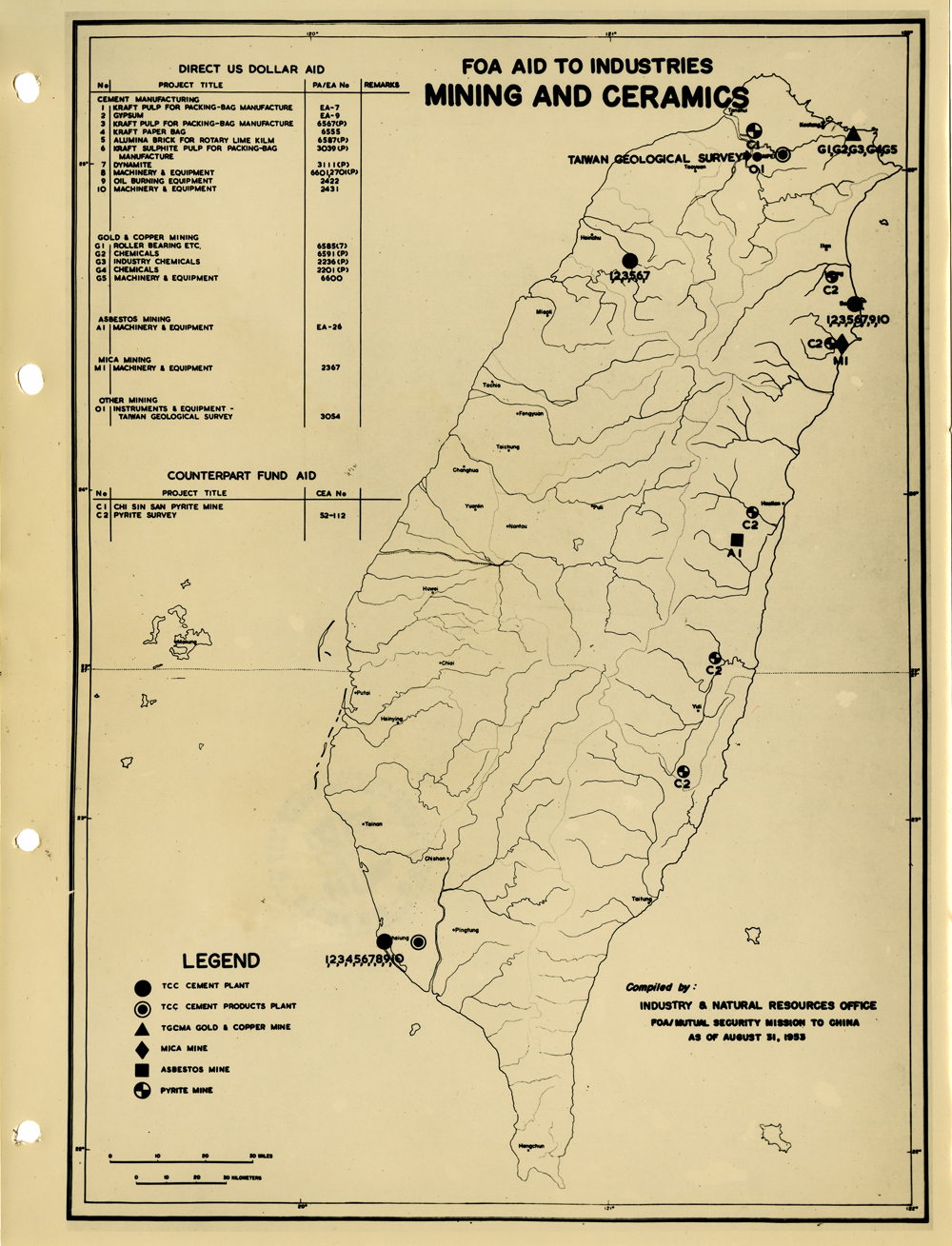
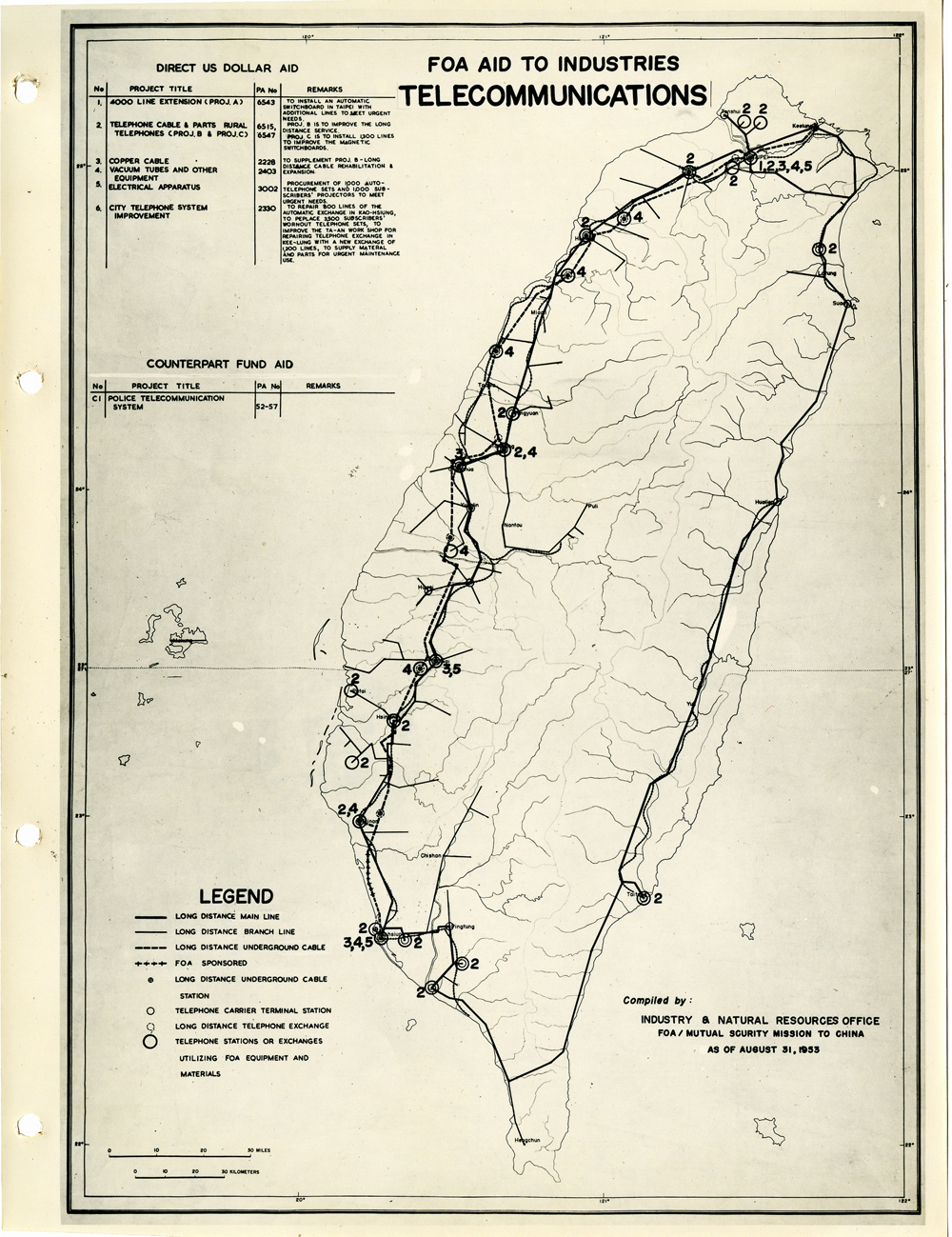
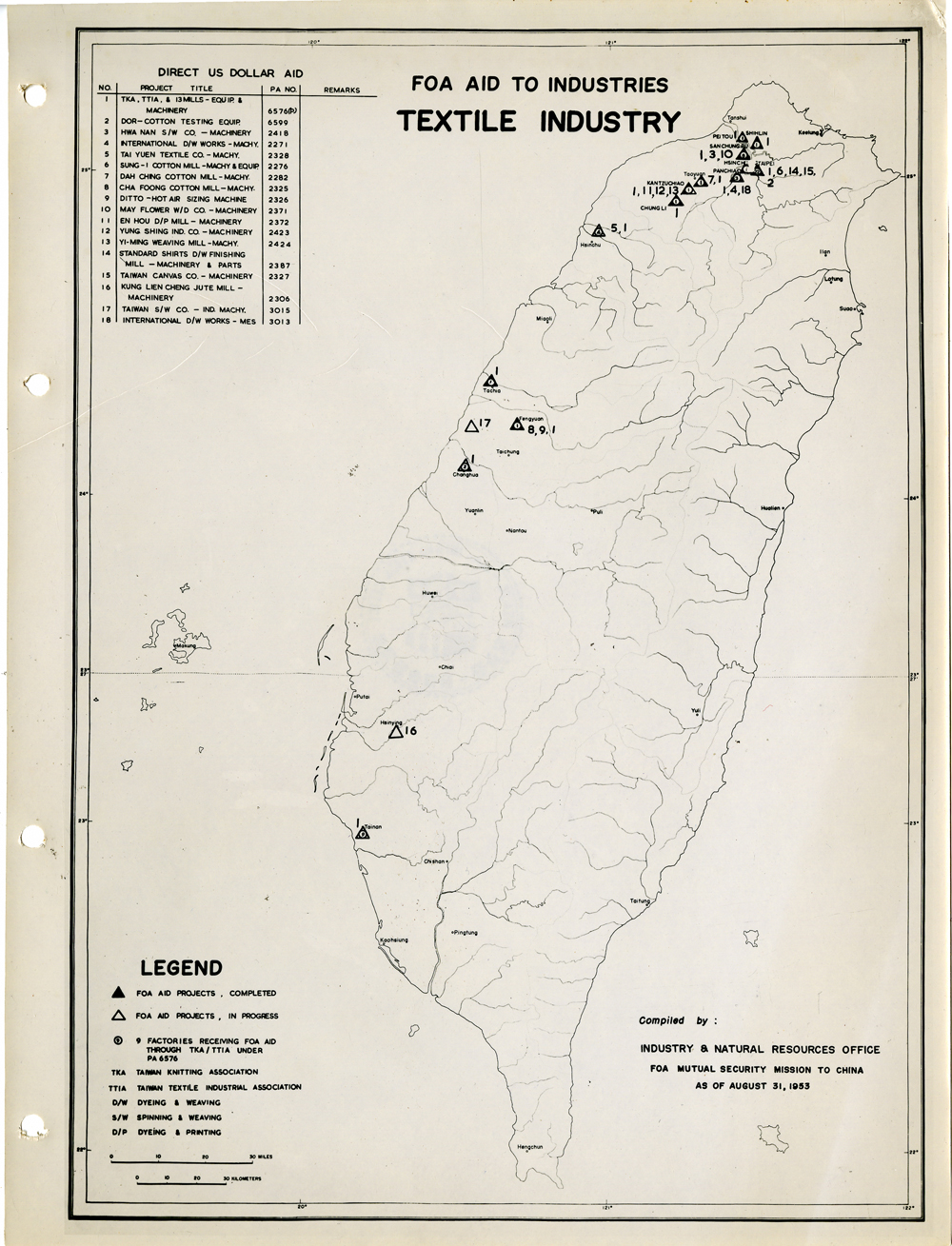
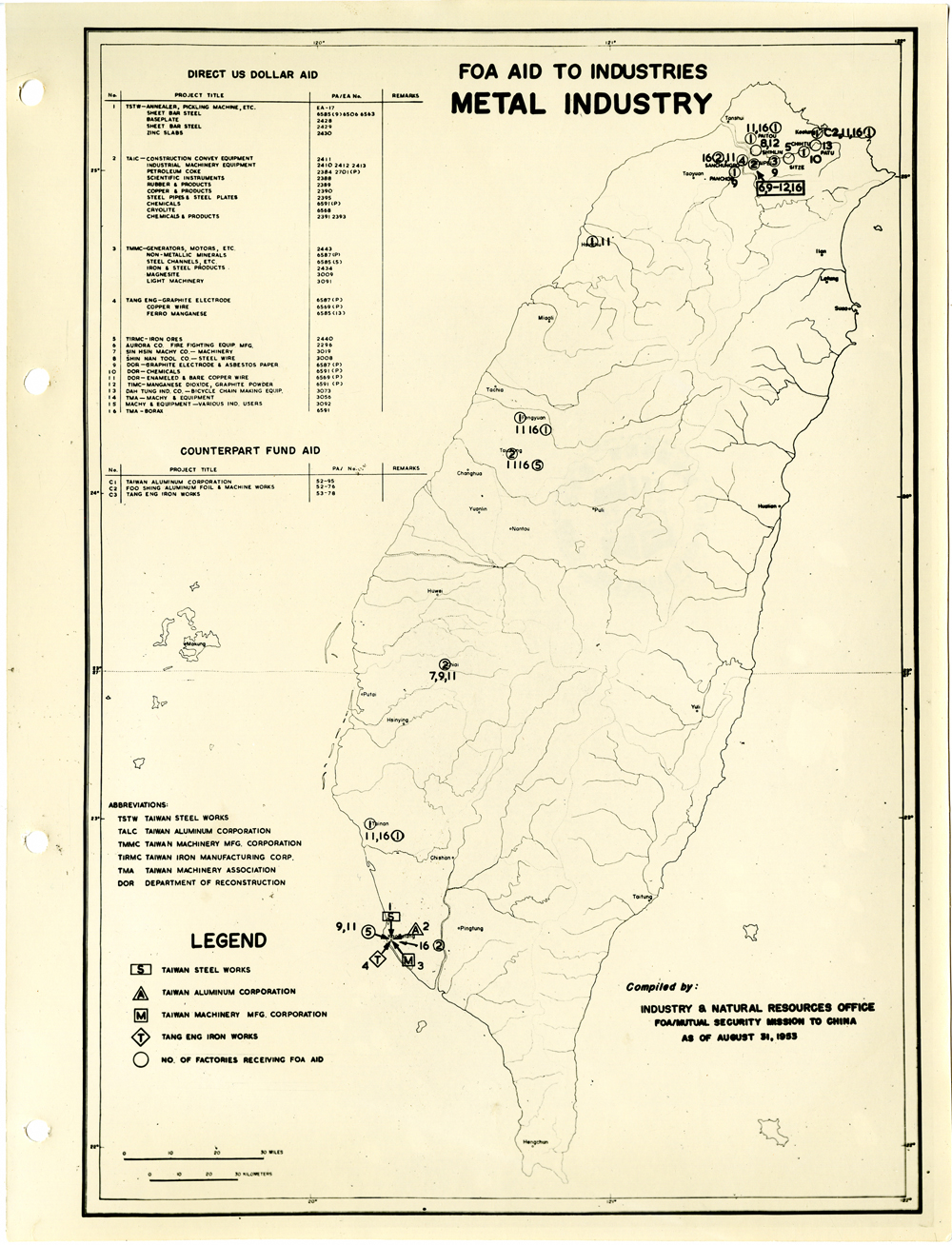
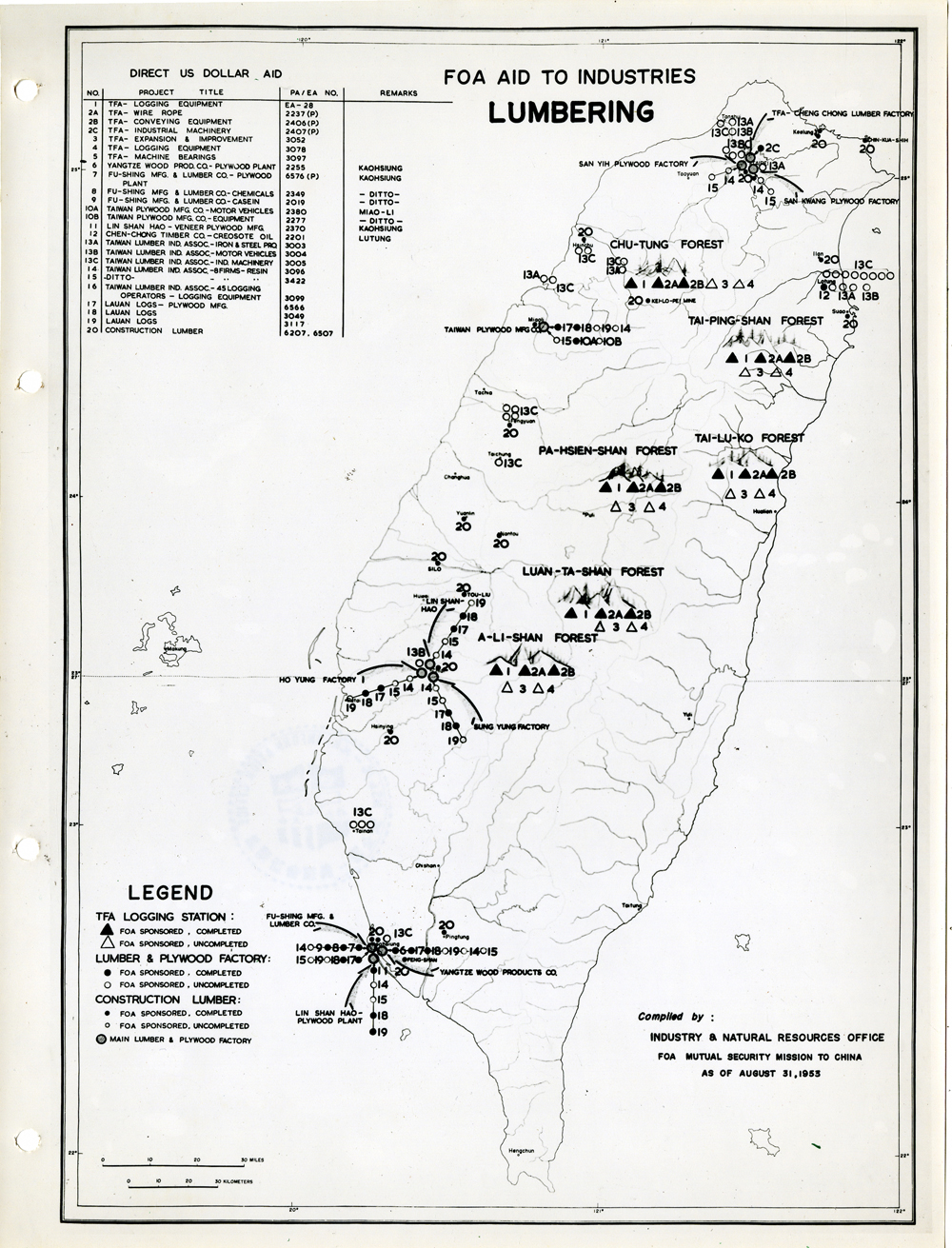
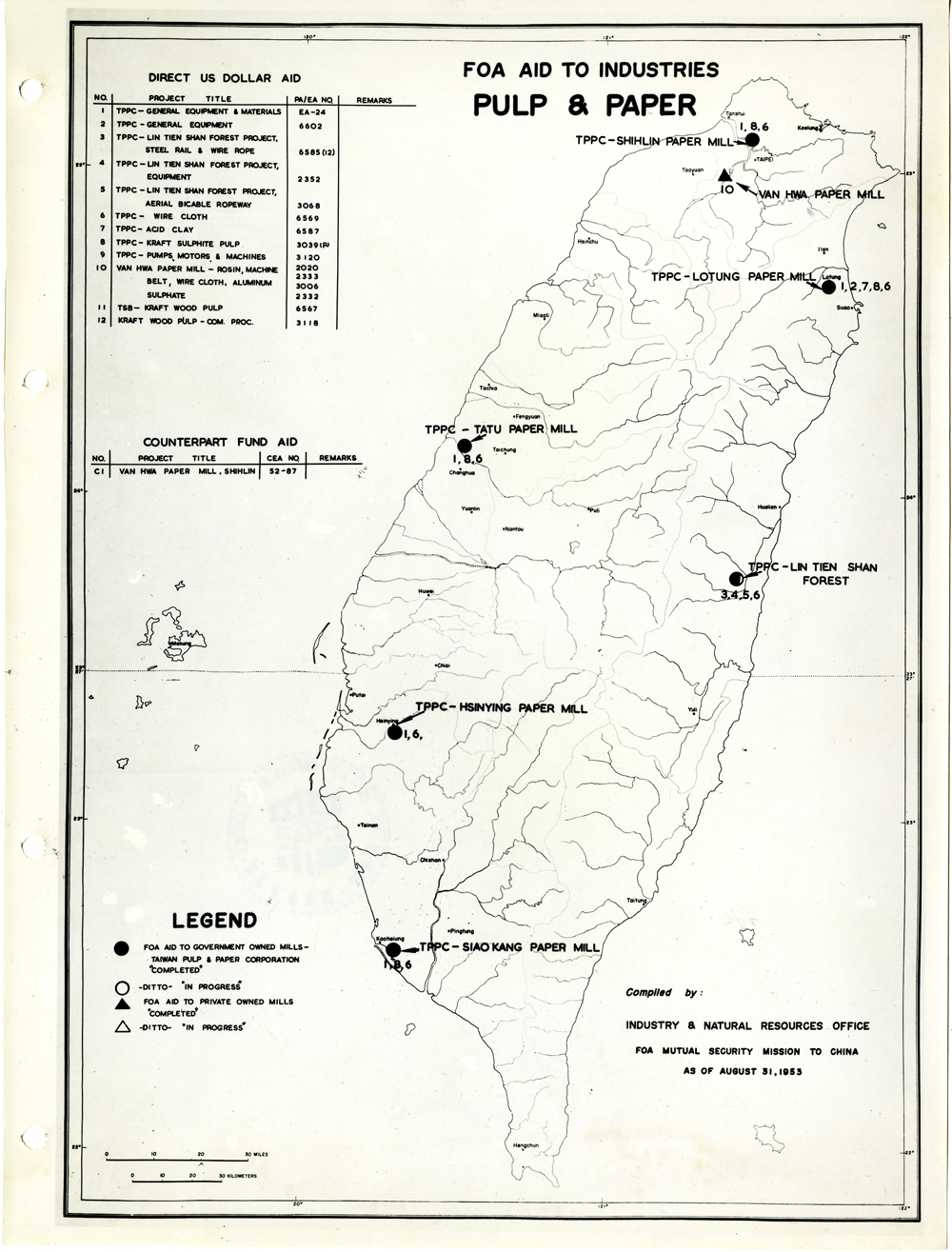
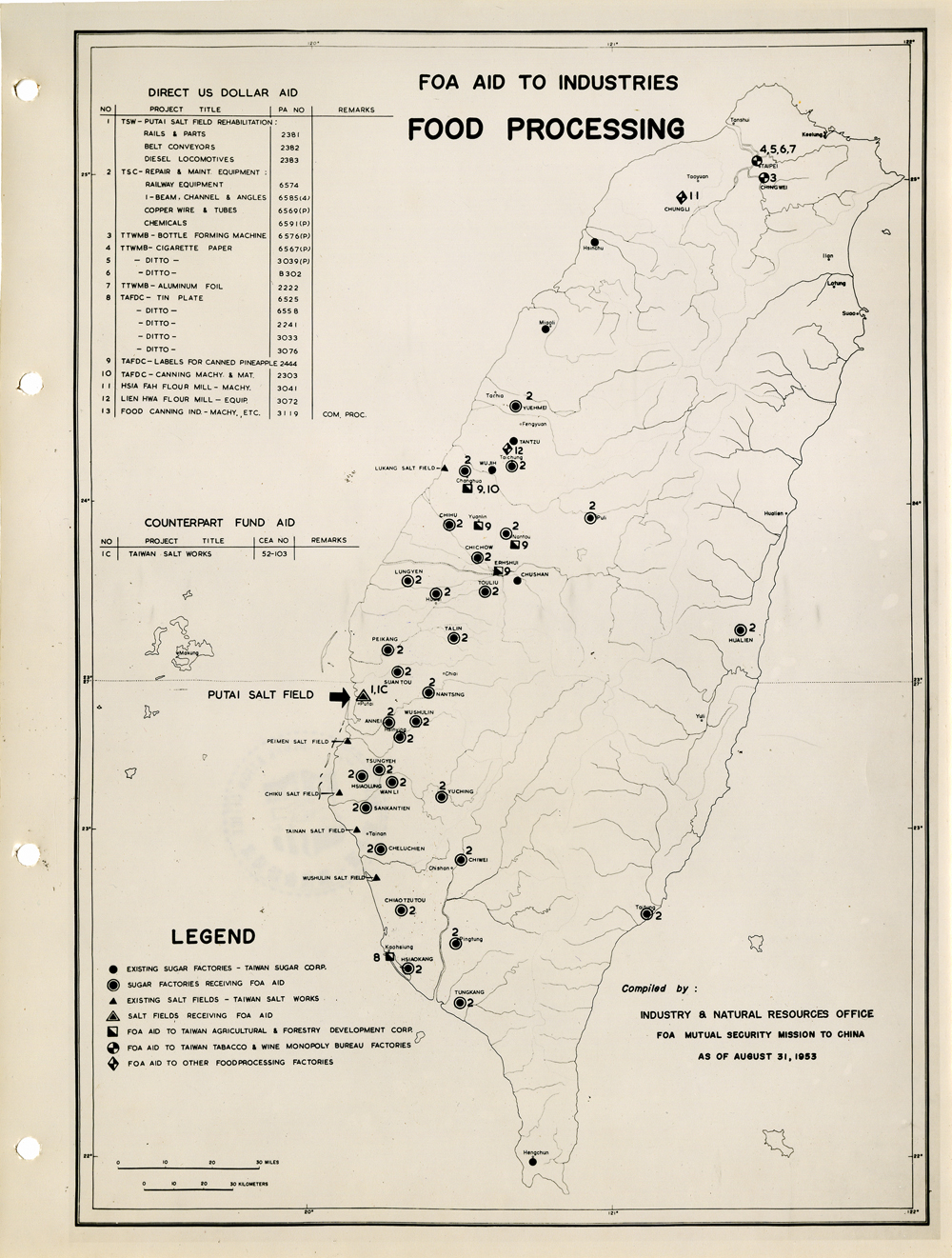
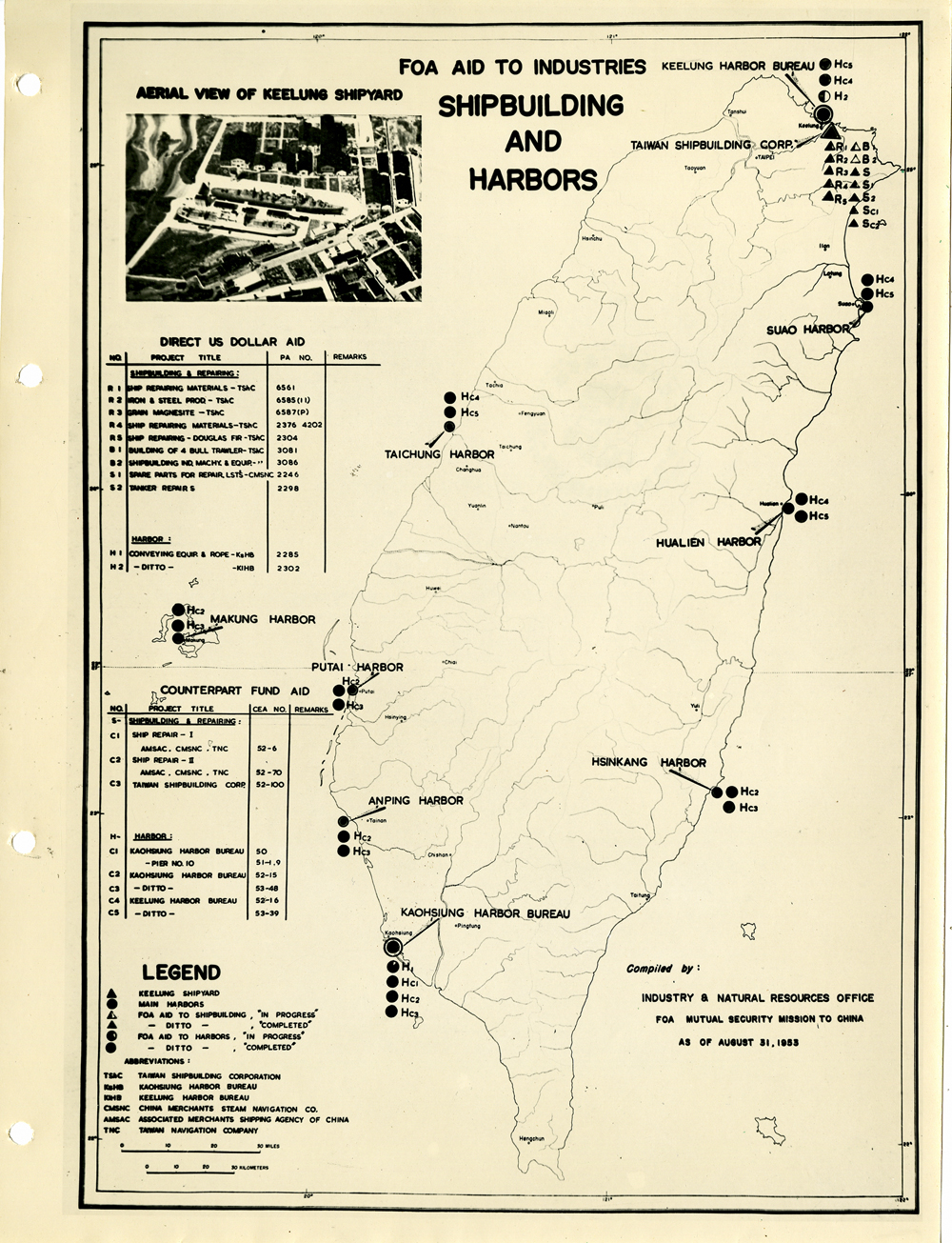
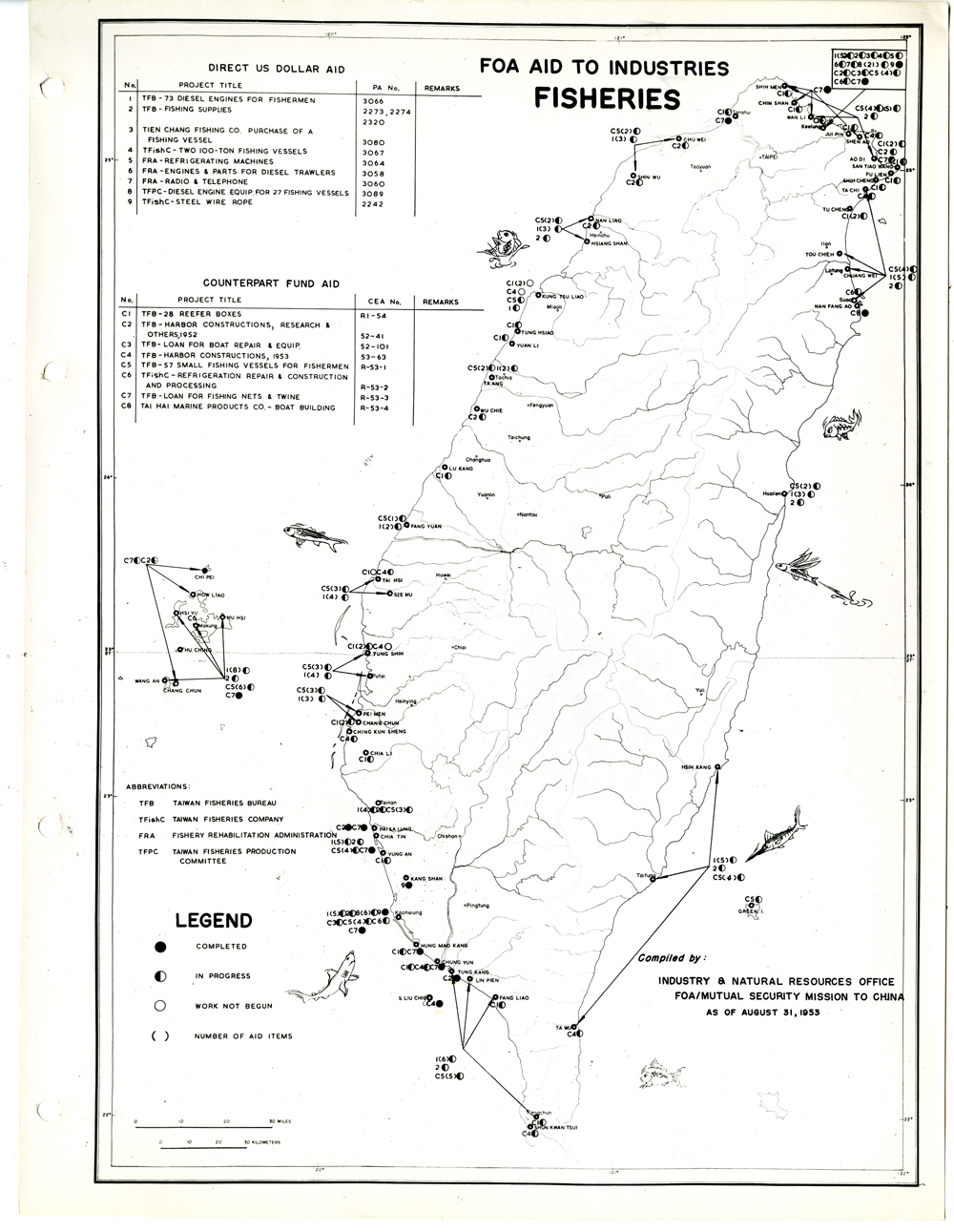
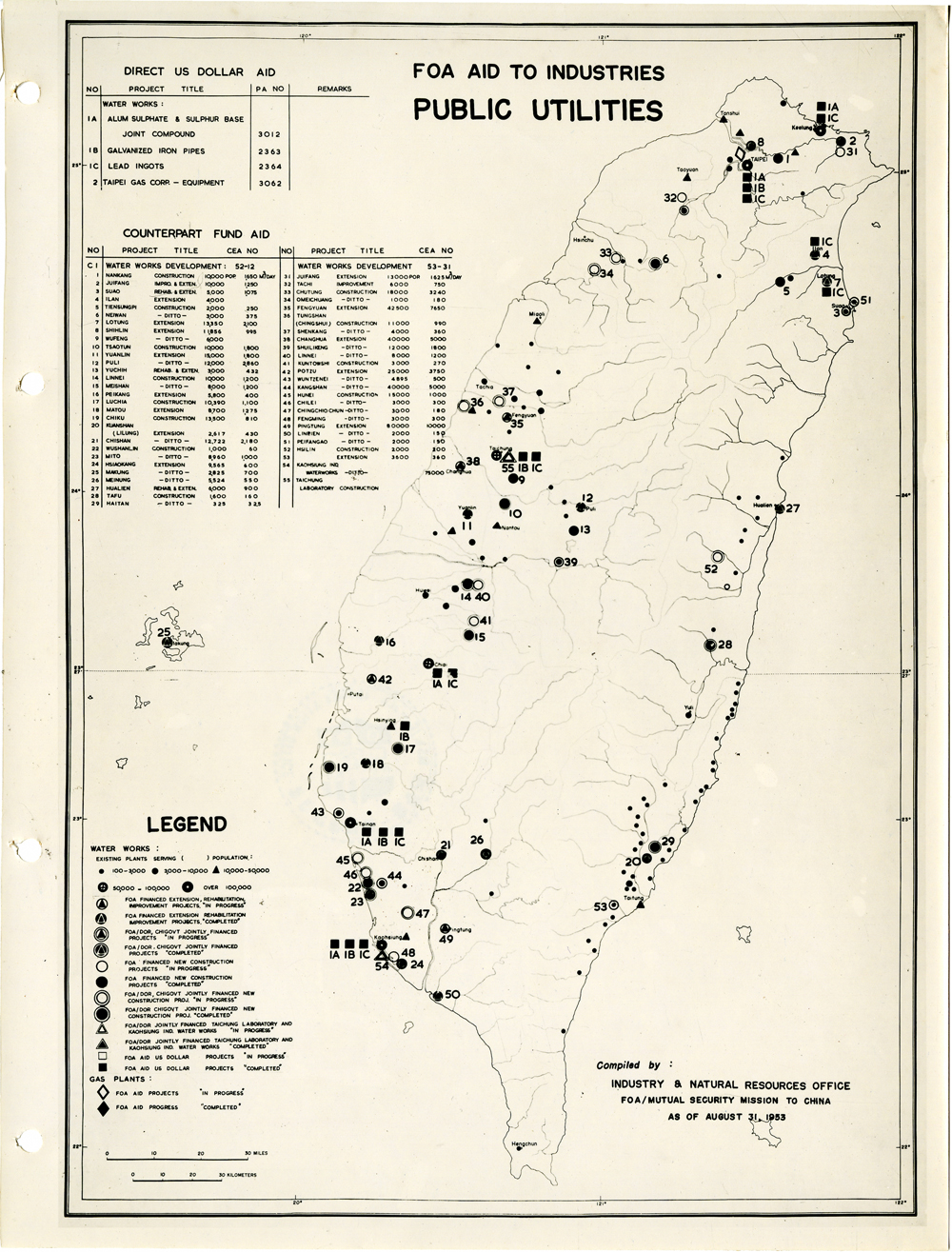
當時美援對於臺灣建設的規劃是多方面的,包括電力,鐵路,公路,肥料,煤礦,陶瓷,電信,紡織,化學工業,金屬,伐木,造紙,食品加工,造船,港口及漁業(Power, Railways, Highways, Fertilizer, Coal Mines, Mining and Ceramics, Telecommunications, Textile Industry, Chemical Industry, Metal Industry, Lumbering, Pulp & Paper, Food Processing, Shipbuilding and Harbors, Fisheries)等多方面的建設、開發、或建廠。而在各建設中所投入的資金也事先充分規劃,是由「直接金援」(Direct US Dollar Aid)與「相對基金」(Counterpart Fund Aid)兩種不同形式之援助資源共同支援的。臺大圖書館的《狄寶賽文庫》中所包含的16張美援臺灣建設規劃地圖,清楚呈現經美國的國外業務總署核定的臺灣各種建設分佈圖以及所要投入各種建設之「直接金援」與「相對基金 」之比例 (參看下方影片 1) 。此批美援建設地圖除了提供了解美援運作上之金援分配規劃之外,也提供學者可以就美援之建設規劃與落實情形進行研究、甚至進行美援臺灣建設之規劃與臺灣後來的十大建設之比較研究的原始素材。
In 1945 at the end of World War II, Japan’s defeat meant Taiwan came under control and administration by the Nationalist Government. Air attacks on Taiwan during the war period left damage all over Taiwan. Therefore, in the civil administration’s initial period it was faced with the huge cost of reconstruction and social development. Fortunately, starting in 1950, support in the form of foreign aid from the US government, executed through “Chinese-US Cooperation”, allowed the smooth development of infrastructure construction.
The use of so-called “US aid” was planned for Taiwan by the Economic Cooperation Administration, Mission to China (ECA) and the Executive Yuan’s US Foreign Aid Committee. They organized a variety of construction work. In 1951, the ECA became the Mutual Security Mission to China (MSA) and in 1953 it changed its name again to Foreign Operations Administration (FOA). That led to planning and documentation relating to US foreign aid using the names ECA, MSA, and FOA.
At the time, the plans for the use of US foreign aid covered a variety of areas including the establishment, development and construction in power, railways, highways, fertilizer, coal mines, mining and ceramics, telecommunications, textile industry, chemical industry, metal industry, lumbering, pulp & paper, food processing, shipbuilding and harbors, and fisheries. The necessary capital was provided in the form of so-called Direct US Dollar Aid and Counterpart Fund Aid. National Taiwan University Library’s “de Beausset Collections” includes 16 maps of US foreign aid plans, clearly showing a variety projects in Taiwan approved by the US administration and the proportion of Direct US Dollar Aid and Counterpart Fund Aid to be invested for each project (watch the video 1 below). These US aid construction maps not only provides an understanding of how US foreign aid was put to work, it also provides scholars with material for research on the planning and implementation of the aid. It can even be used as source material for comparisons with Taiwan’s ten major infrastructure projects.